Rank Recovery
2024 update by Bob Sakayama, CEO TNG/Earthling, Inc.
Bob Sakayama is CEO of TNG/Earthling, Inc., a technically robust SEO consultancy based in New York City known for their live site research and their ability to deliver high ranks and traffic to businesses & organizations reliant on the search. His clients also include other SEOs. More on Bob is here.
20 February 2024 How we know negative seo is real
Revitalizing underperforming sites
We're seeing many older websites that used to dominate the search falling into hard times as their rank/traffic metrics gradually sink to new lows after peaking 2 - 3 years ago. Frustrated owners have scoured the potential causes and see only a mystery or suspect a Google penalty.
Unlike 10 years ago, I'm not seeing any actual Google penalties - where you see a notice of a manual action in Search Console. But I am seeing collapse. And the victims are established businesses. And although the decline may have been stretched out over months/years, it still feels like a penalty. Diagnosing this ailment is what we do. By the time we're engaged, the client and their SEOs have already hit all the low hanging fruit, so our task is off the beaten path, leaning on experience, forensics and intuition. Many sites have simple code errors that remain hidden because no one's looking for them, and most developers have only a cursory knowledge of search. Simple oversights/errors can have outsized consequences when scaled. Another frequent cause is blowback from an earlier attempt to optimize the site using tactics that once worked but have aged poorly. Google-penalty.com reveals some causes that we've seen on multiple sites not commonly understood by SEOs.
For this post we're focused on recovering an older, underperforming site - chart below, displaying data over 1 year. The business is a retail apparel merchant in a very competitive market - pop culture.

Note that the all time highs in traffic growth is accompanied by a similar growth in keywords ranking in the top 100.
Because the site was previously optimized with links, a good amount of time was spent cleaning the link profile before making any changes. In response to the recent growth of widespread negative seo, we routinely run bots that flag links associated with attacks. I find it stunning to find that most productive sites are targets of these unethical attacks. These and any other sketchy link sources get disavowed in Search Console.
Optimizing using Adjacent Content
Once obvious technical and link vulnerabilities were removed, the structure was reorganized for building content. This model has proven itself in the past but now we're using AI to scale it. Adjacent content is the driver of this strategy, structured as below:
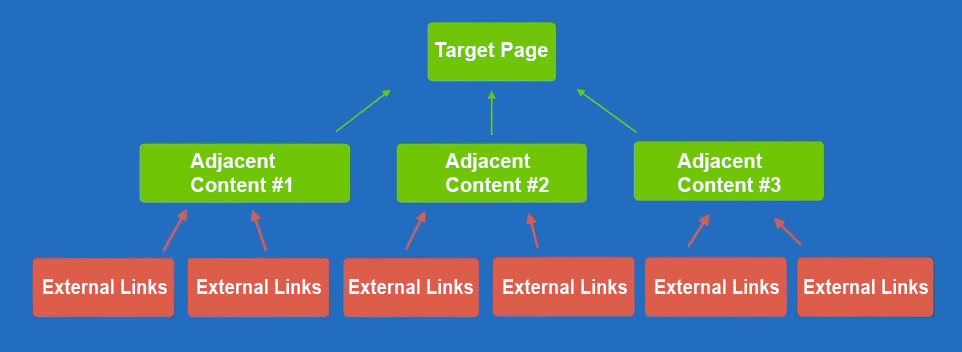
The above power center represents the adjacent content model that is currently being implemented. The target page is semantically optimized for valuable keywords including the primary keyword target. Adjacent content directly supports the main target by introducing informative content on related topics.
A version of this model was always in play, but the use of AI tools has made the creation of large, content rich power centers easy and cheap. The more unique & informative content deployed within this structure the better. With appropriate topics, there's really no limit to the amount of content you can create and use this way. The semantic relationship to the target, the quality of the adjacent content, and the appropriateness of the topic make this work. These structures create a focused content silo that conveys relevancy by aggregating information semantically organized to benefit the entire site for a growing number of related keywords.
This structure follows the content relevancy model as outlined in Google's patent application - patents of March 2020 - which spells out their hierarchy of categories, linked content & semantic relevance. It's a logical organization of information and a roadmap for connecting related content in a way that best conveys its relevancy. By emulating this model and continually developing useful content, we can grow the authority of the target page.
Creating and growing authority means actually delivering a lot of valuable information. Quality matters. Adjacent content needs to contribute to an understanding of the main topic without being redundant or repetitive. Presentation matters. Creating a good read is essential because useful content actually gets read and holds ranks.For the work involved creating this structure, AI has become indispensable. Managed well, it can assist with topic discovery, gathering information, and content generation. I have a relevant post here: Using AI for SEO
Notice that external links never point directly to the target page. With a limited number of links, on small sites or in less competitive environments, linking directly is effective. But in a competitive space, with the link numbers at scale, too many powerful links pointed to one place always triggers a negative response. My experience on this site demonstrates that a concentration of link equity is a red flag.
Why this works
The problems triggered by SEOs using links at scale are mostly associated with overuse or misuse on some level. Amounts matter, as does timing. We can't use too many dofollow links, valuable anchors, absence of nofollows, links posted too frequently, etc. There are critical red lines associated how links are used that we need to avoid. This model avoids these problems using the Degrees of Separation principle. A link from the NYTimes is super powerful. A link from a site that has a link from the NYTimes is one degree of separation away from an authority, but some of that authority gets passed across the link. Using this model external links are not pointed directly at the target page. Instead the links point to the adjacent content, which then points to the target. This separation makes linking safer, and actually more powerful. It's true that the external link equity passed to the target page is less because it's second hand, but that equity is now cumulative from multiple sources and still focused on the target while distributed across the entire site.The power center insulates the target from being seen as over-optimized because it never receives any external links - all the link equity is coming from internal links. And that equity is distributed, not concentrated only on one url. The distribution also ensures that the related topics also gain authority, expanding the keyword reach of the site.
If you build a power center around really useful/valuable content, you may not need the links to make this work, especially if you can establish a readership for your content and inspire organic link growth as a result. But powerful links can supercharge the effectiveness and significantly improve the performance.
How we know negative SEO is real
This chart below is from the same site as above, but shows the seven year organic performance - a lot of ups and downs. Because we control every aspect of this site, including the links, this result is basically an experiment that proves that negative SEO is real. Those ups and downs were caused by our focus on powerful links as the primary optimization strategy. We attempted many different linking tactics, each time succeeding short term followed by a stunning collapse. That's why the chart has peaks and valleys in the extreme.

Except for that last steep climb, this is what a series of failed efforts looks like. But there's a silver lining to those failures - seven years worth of data revealing some uniquely important information. The experiment is designed to inform us on Google's red lines, when using a large number of the authoritative links. After each collapse, the link profile was adjusted. Variables like the inclusion of nofollow anchors, naked urls, brand anchors, images anchors, all worked until some unknown volume threshold - the biggest red line - is reached. But in spite of the attempted variations we ALWAYS crashed. So pretty clear it's just the numbers.
What's most important is knowing how the links were used, and how that use impacted the search. Every one of those steep climbs and accompanying collapses was triggered by an action we took.
We already know that links can move the ranks up. But the fact that certain conditions cause ranks to collapse suggests very strongly that negative SEO is real. Clearly there are actions we took with our links that eventually crossed the red lines. But we always recovered and never saw a manual action, so these downdrafts are not actually "penalties", but that's just semantics. We can trigger these downdrafts. If it's done intentionally that's negative SEO.
So in spite of Google's claims, we know that negative SEO is real. And from work on client sites, we know from seeing the evidence of actual attacks that it's growing.
In some cases we have been able to correlate rank/traffic improvement following the submission of disavows. One of the problems in trying to track this is that Google claims to be able to spot links from bad sources or posted with bad intent and ignore them so they do no harm. If the domains in your disavow are discounted already, you will see no improvement. But because there's strong evidence that disavowing attack links can be effective it should be done by default. I don't trust that Google has negative SEO under control. It's a service being strongly pitched by unethical SEOs and the idea of taking down your competition is very tempting - it's cheap, you remain anonymous, little chance of blowback.
Intriguing footnote
During our experiments, one of the biggest surprises we encountered was the newly enabled capability of nofollow links - my post is here: Changes to nofollow. Turns out that nofollow links now appear to convey relevance and in some documented cases actually push rank/traffic.
2021 update by Bob Sakayama, CEO TNG/Earthling, Inc.
AI
It's the kind of seismic change that has largely gone unnoticed even as its influence mushroomed. The introduction of artificial intelligence into the growing data capabilities of every industry, has been the invisible hand disrupting the old ways and providing better outcomes by using machine learning to optimize tasks and automate decision making.
The recent release of ChatGPT and GPT4 have been getting a lot of attention but these viral tools are just the tip of the iceberg.
The AI assimilation has long been underway. Individually developed systems can be trained to perform seemingly unrelated tasks, like this pastry shop AI that initially learned to identify pasty by shape and color. Using basically the same kind of visual rules it used on the pastry, it was later trained to identify cancerous cells. AI is everywhere and has for some time been making often significant changes to every aspect of life.
And that includes Google's search results. A long stated goal of Google is to actually understand why the search terms were used so they could provide more useful answers. The intent or motive behind the search terms is the holy grail. Training AI on the search semantics is how they are achieving this goal, enabling high probability interpretations of the meaning and the context using data science, by training the machine to accurately guess the reason for the search.
If you are a student of the search you already know that changes to Google's algorithm happen very frequently, and it's impossible and unnecessary to keep track. Most are minor tweaks that don't impact most sites. But some changes create disasters and need to get walked back quickly - loss of ranks is an existential crisis for businesses harmed, and the resulting public anger together with the embarrassing bad press are hugely motivating. That's the major reason their "hyper-local" change happened so slowly. Hyper local showed search results first filtered by closeness to the searcher. It was an improvement for pizza searches but disaster for sites with a national aspirations. Often, Google makes algo changes contrived to correct a problem - eg. the payday loan scams, or seos gaming Google. They recently made huge changes to address the liability in providing search results that could potentially end up harming people. The "Your Money of Your Life" sites sold products or gave information to users where a high ranking site created a liability for Google if it sold harmful or bogus product or gave ruinous financial advice. The algo changes required these YMYL sites to provide more evidence of their authenticity before permitting them to rank well. AI is used to identify YMYL businesses that need a higher level of scrutiny before ranks are awarded.
It only makes sense to apply AI to the semantics of the search query. And that process has been underway for long enough to become noticeable. The result is a deeper understanding of semantics, and natural language process - the association of intention & motive with words. Google has always been a semantic search engine. Once it determined ranks by identifying matching strings of text. The AI attempt is to determine ranks by matching intent.
Applying AI to Semantics
Semantics will always be a core study of the Googlebot and while how it evaluates the words will change, the importance of the motive behind the search has always been the objective. Search relies on languages, which can relate differing ideas and meanings to the same words. With enough supporting information, semantics can become a window into the actual meaning of the words being used. Matching the intent with the search results rather than matching a string of text, is the next generation of search. Where, by having access to huge amounts of data regarding the words being searched, Google may accurately assess that your search for "serendipity" was looking for a movie, and not a definition. This requires AI. Google has been improving its ability to recognize the real motive and meaning of a query, and this has been gradually altering the search results. But the application of artificial intellegence is meaningful because it implies that the rules governing ranks are shifting to decisions and conclusions made by machines trained to recognize alignment with the search engine's rules.From the published portions of the relevant Google patent it has been obvious for a long time that the organization of the information is critical. Their model for the most semantically relevant document addressing the intent of the searcher was one supported by the most robust knowledge base as well as authoritative inbound links. This has always been the case when described this generally.
What has changed is the sophistication level of the algorithm, which can now reference previous searches, clicks, etc. enabling a better read of the intent of the search. In a former world, the semantic relationships were string based - the same set of words or phrases might match those terms used on another page which would then rank high for those matches.
The amount of information available around any given search term is staggering. This would include some obvious things like historic data about the searcher, language connections between semantics and meaning, data relating idioms and vernacular to meaning, data on synonyms, slang, etc., etc. Machine learning, or artificial intelligence applied to understanding searches can make highly reliable predictions regarding search intent. Because now the search semantics can be compared to other search results that share meaning, but not spelling. It's no longer matching the words searched, but the meaning.
Google has had many years to integrate AI into its systems - especially when you consider that machine learning began in the 1950s. But it's pretty obvious that their success has been spotty. For example, the search results for "books by children" has no books written by children, only children's books when searched in September 2021. But this result may be intentional given the relative Google Ads revenue generated by searches for "childrens books" vs "books by children".
But they are getting better at it. Frequent Google users know the search results have been improving. As the search engines get this right, their results become more valuable.
Changes to The Impact of Nofollow
The other changes underway involve the use of AI to detect efforts to game Google's search results. Some of these impact SEO directly. The most significant very recent change is the transformation of nofollow links from worthless to valuable. This corrects a long overlooked flaw in the handling of text links from other websites. Google encouraged the tagging of certain text links "nofollow" which meant the Googlebot would not crawl the link - it would be ignored and no link equity will be passed. Text ads would need this tag so paid links could not push rank. Paid links that ignored this rule could get the site penalized in Google. This rule has been in place for many years and it is standard practice to tag a sponsor's text link as nofollow.
But very recently, Google made a philosophical change regarding nofollow, adding some qualifiers to the tag, and recognizing the value of a nofollow link in providing information useful for the search results. "Sponsored" and "UGC" can now be added as additional qualifiers to convey an ad and user generated content. But more important than the effort to get more granular information from webmasters is the change that will most impact SEO going forward.
We started running tests on this as soon as we learned about the change, early 2021, starting by actively grooming the nofollow links we control, like all those paid text ads, to use valuable keywords. These experiments have not yet moved the needle - we're seeing no rank improvement when adding nofollows to an existing link profile.
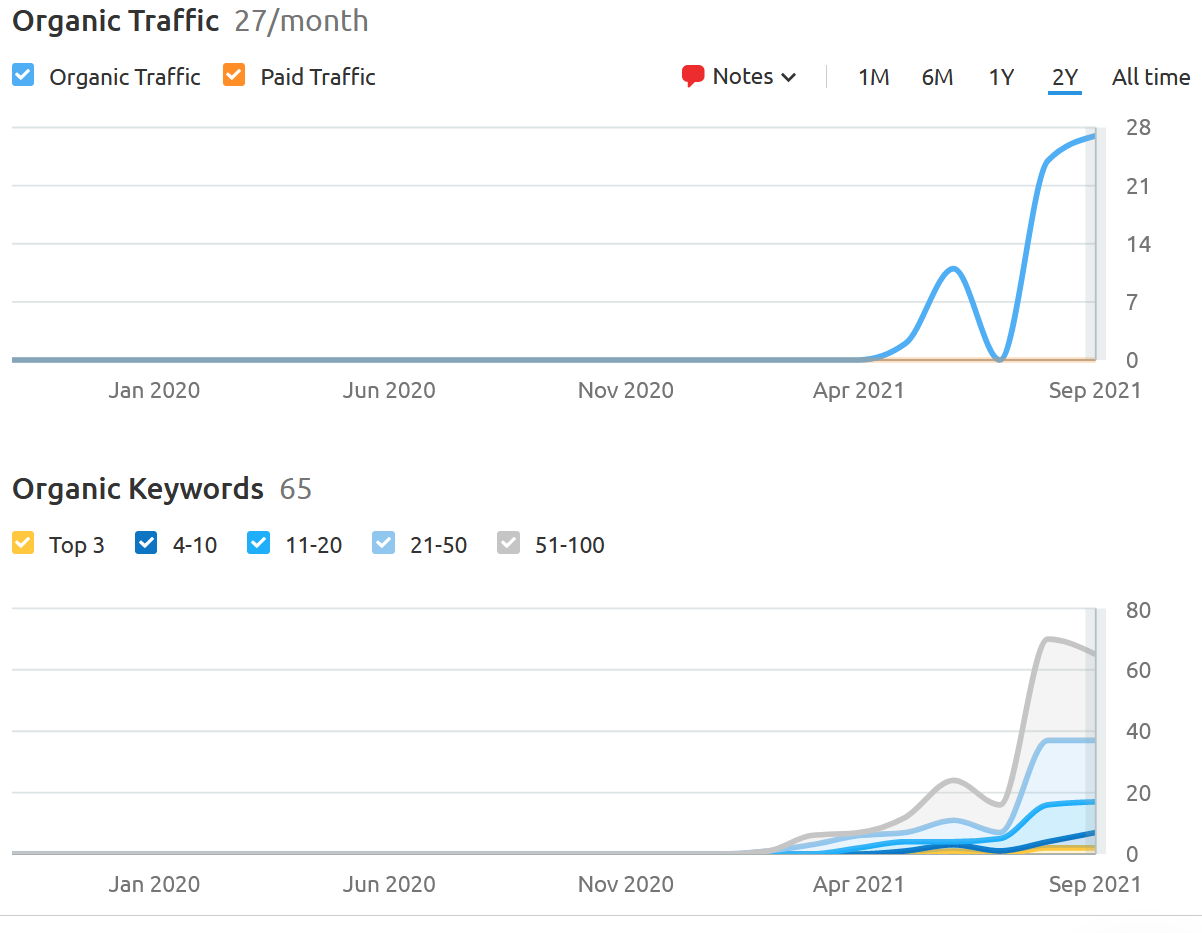
But there's one experiment that is very telling because it was with a relatively new site, and the only links on important keywords were nofollow. 3 months after the links were added the site's organic traffic started hitting new all time highs. This first experiment with important results involved a local consumer service business. Below is the organic traffic chart from SEMrush for their website. The experiment was to use only nofollow links from reasonably authoritive domains. In the chart below, links were added about the time of the first bump in June 2021 when 25 nofollow links on valuable anchors were posted without either of the 2 new qualifiers.
This was an all in experiment, meaning only the anchors of the nofollow links carried important semantics in an attempt to see if Google will use those semantic signals in their search results. It makes sense to use information from ads to determine the nature of the business buying them. If a company has a lot of nofollow ad links with anchors on "widgets" it's pretty clear that's an important semantic for them and their ranks should indicate this. But there is a risk here that Google is definitely aware of as they elevate the status of nofollow. Google has long claimed that money can't buy rank. So Google may not want to be revealed to be enabling paid, nofollow text links to positively influence ranks, but that is what appears to be happening here.
At this point in time we don't know enough to make any kind of claim regarding SEO tactics using nofollow. But this experiment is definitely revealing something important and future experiments are already underway to discover how we can make use of this major change in Google's handling of nofollow.